Patrick McCullough, Extension Weed Specialist, University of Georgia
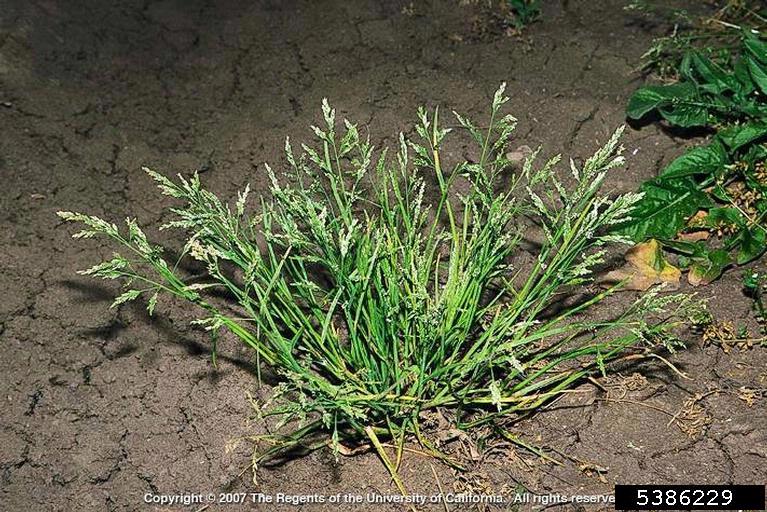
Preemergence herbicides may prevent annual bluegrass infestation via seed and limit current infestations from further spreading. However, preemergence herbicides will not eradicate established plants and will not effectively control perennial biotypes of annual bluegrass from spreading vegetatively.

Application timing of preemergence herbicides for annual bluegrass control is very important. Herbicides must be applied in late summer/early fall before annual bluegrass germination. This info on timing herbicide application is taken from an article online by Tim Murphy, UGA Weed Scientist. “Annual bluegrass germinates in the late summer and early fall when daytime temperatures consistently drop into the mid-70os and nighttime temperatures are in the mid-50os for several days. In the Piedmont of Georgia for winter annual weed control, apply the preemergence herbicide sometime during the first two to three weeks of September (by September 20). In north Georgia, the last week of August up to about September 15 would be the preferred time. In South Georgia, the application should be made during the mid-September to mid-October time frame.”
A second herbicide application can be applied in spring to control germinating plants. Fall applied preemergence herbicides cannot be used if reseeding or re-sodding is needed to repair areas of damaged turf within several months after herbicide applications.
Several preemergence herbicides effectively control annual bluegrass in fall and winter which are similar to products used for summer annual weed control (Table 2). These herbicides include dithiopyr (Dimension), oxadiazon (Ronstar, Starfighter), pendimethalin (Pendulum, others), and prodiamine (Barricade, others).
Combination herbicide products are also available which may improve efficacy of applications. These products include oxadiazon plus bensulide (Anderson’s Crab and Goose) and benefin plus oryzalin (Team 2G or Team Pro). Many preemergence herbicides are available under a wide variety of trade names and formulations. Carefully read and follow label instructions before applying products.
Most preemergence herbicides will provide similar initial efficacy if applied before annual bluegrass germination and if sufficient rain or irrigation is received. Preemergence herbicides require incorporation from irrigation or rainfall so that weeds may absorb the applied material. In order to effectively control annual bluegrass, preemergence herbicides must be concentrated in the upper 1/3 inch of the soil profile. Avoid herbicide retention on leaves and incorporate the herbicide into the soil by irrigating turf immediately after application.
Table 1. Efficacy of postemergence herbicides for crabgrass control in turfgrasses. See labels for turf tolerance and areas for use.
|
Postemergence Herbicides for Crabgrass Control |
||
| Common Name | Trade Name (Examples) |
Control |
| Clethodim | Envoy |
E |
| Fenoxaprop | Acclaim Extra |
E |
| Mesotrione | Tenacity |
F-G |
| Quinclorac | Drive, Drive XLR8 |
E |
| Sethoxydim | Segment, others |
E |
E = Excellent (90 to 100%), G = Good (80 to 89%), F = Fair (70 to 79%), P = Poor (<70%).
Table 2. Efficacy of preemergence herbicides for annual bluegrass control in commercial turfgrasses.
|
Preemergence Herbicides for Annual Bluegrass Control |
||
| Common Name | Trade Name (Examples) |
Control |
| Atrazine | Aatrex, others |
E |
| Benefin | Balan |
E |
| Bensulide | Betasan, others |
F |
| Dithiopyr | Dimension |
G |
| Ethofumesate | Prograss |
G-E |
| Mesotrione | Tenacity |
F |
| Oryzalin | Harrier, Surflan |
G |
| Oxadiazon | Ronstar, Starfighter |
G |
| Pendimethalin | Pendulum, others |
G |
| Prodiamine | Barricade, Cavalcade, others |
E |
| Pronamide | Kerb |
E |
| Simazine | Princep, WynStar, others |
E |
E = Excellent (90 to 100%), G = Good (80 to 89%), F = Fair (70 to 79%), P = Poor (<70%).
Helpful publications from UGA Extension on controlling annual bluegrass
Annual Bluegrass Control in Residential Turfgrass
Patrick McCullough, Extension Weed Specialist
This publication describes methods of control for annual bluegrass in residential turfgrass lawns.
To see the entire publication go here.
Topics:
Annual Bluegrass Control in Non-Residential Commercial Turfgrass
Patrick McCullough, UGA Department of Crop and Soil Science